Case Study
Rapid Serological Testing for COVID-19 IgG
Test Platform
Delta Life Science introduces a platform that enables rapid and cost-effective development of new diagnostic tests. This platform can be employed to swiftly respond to the demand for a new test, such as in the case of emerging epidemics. Delta Life Science’ biosensor technology, based on photonic integrated circuits, enables quantitative and extremely sensitive multi-biomarker detection in small patient samples in a matter of minutes.
Antibody Test
A rapid serological test for the detection of antibodies can be used to determine if a person has had an infection and potentially developed immunity. However, current point-of-care tests are limited in performance and not recommended to be used for individual patient diagnostics.
As a technology showcase, Delta Life Science developed a rapid COVID-19 IgG test by immobilizing the Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2 on its proprietary optical chip. One of the great advantages of Delta Life Science’ platform is label-free detection, allowing to directly and quantitatively detect binding of biomolecules. This is shown in Figure 1, displaying the signals from different IgG monoclonal antibodies binding to the RBD-coated chip, where antibodies present in higher concentrations and/or with a higher affinity produce higher signals.
Subsequently, the RBD-coated chip was challenged by a blind panel of 10 sera provided by Reinier Haga Medical Diagnostic Center (RHMDC). The samples were drawn from healthy individuals (pre-COVID-19 pandemic) and individuals with PCR-confirmed COVID-19. The PCR-confirmed sera were reference-tested at RHMDC using the Wantai total antibody test (WTA-test). The panel was sequentially analysed on Delta Life Science’ point-of-care development platform. Between consecutive sera, the chip was regenerated. This effective regeneration procedure allows for rapid testing without replacement of the chip.
The time-to-result was less than 15 minutes per sample.
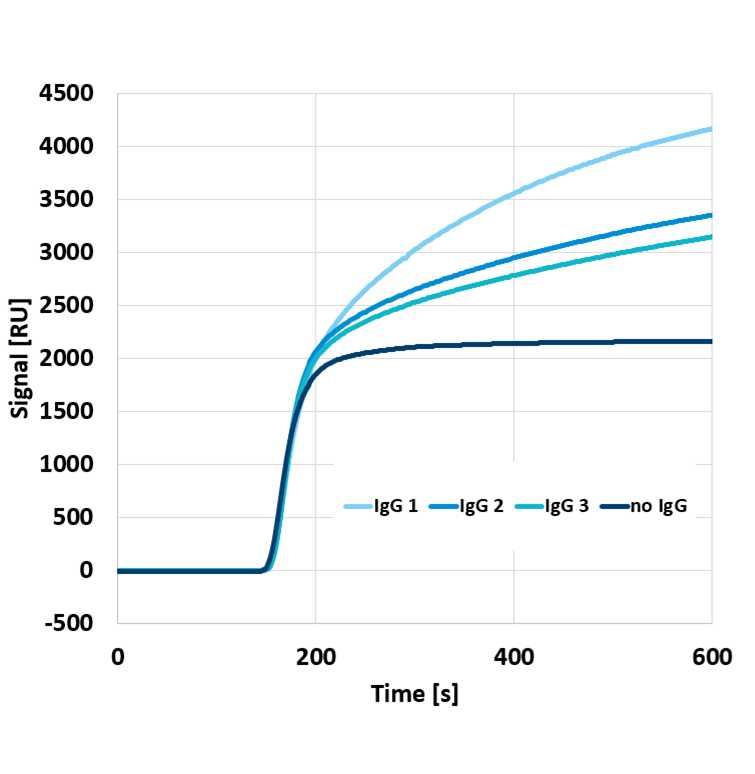
Figure 1: Sensor signals for different validation samples containing different quantities and types of IgG antibodies.
The unlocked panel data in Table 1, obtained after completion of the analysis, shows for each sample how many days after a positive PCR the serum sample was drawn, the WTA-test results for PCR-confirmed samples and the results obtained with the Delta Life Science test.

Table 1: Blind panel test results for Delta Life Science’ test and the Wantai test.
The panel consisted out of 5 sera drawn before the COVID-19 pandemic, classified as negative, and 5 sera of individuals with PCR-confirmed COVID-19, classified as positive. Results of all negatives and 4 out of 5 positives obtained with the Delta Life Science test matched the WTA laboratory test. Solely sample 9 tested negative at Delta Life Science, while the WTA-test was positive. This result is likely due to the fact that IgG antibodies are typically developed later than 8 days after onset of symptoms: The WTA-test is sensitive for all immunoglobulins, including IgM which is typically developed earlier, while the Delta Life Science test in this set-up specifically detects IgG.
Next Steps
Currently available point-of-care antibody tests do not have the performance required for individual diagnostic use. As our chips carry multiple individually addressable sensors, it is relatively straight-forward to develop a test able to detect antibodies against different parts of the virus. Such multiplexed tests have been shown to be able to reach very high specificity.
In addition, contrary to current point-of-care tests, our test provides quantitative information about the amount and/or quality of the antibodies, which allows monitoring of changes in a person’s immune status over time.
Finally, the ability of our sensors to simultaneously detect different biomarkers would allow the development of a test that is sensitive to antibodies raised against different virus variants, potentially useful to determine with which variant the patient has been infected, or a test that can distinguish between different antibody types (IgG, IgA and IgM) providing more clinical information.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Reinier Haga Medical Diagnostics Center for providing the reference tested patient sera and our partner Covalab (FR) for providing the RBD and SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies used in this study.
